How Mindfulness Can Transform Your Brain, Meditation has been practiced for thousands of years across various cultures, primarily for its spiritual benefits. In recent decades, scientific research has provided a deeper understanding of how meditation, particularly mindfulness meditation, can profoundly transform the brain.
This guide delves into the science of meditation, explaining how mindfulness practices can alter brain structure and function to enhance mental health and overall well-being.

1. Understanding Mindfulness Meditation
Why It Matters: Grasping the basics of mindfulness meditation helps in appreciating its scientific benefits.
What is Mindfulness Meditation? Mindfulness meditation is the practice of paying focused attention to the present moment, acknowledging and accepting thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. It involves:
- Focused Attention: Concentrating on a specific object, such as the breath, a mantra, or a visual object.
- Open Monitoring: Observing all aspects of the experience, including thoughts, feelings, and body sensations, without attachment or aversion.
- Acceptance: Embracing whatever arises in the moment without trying to change it.
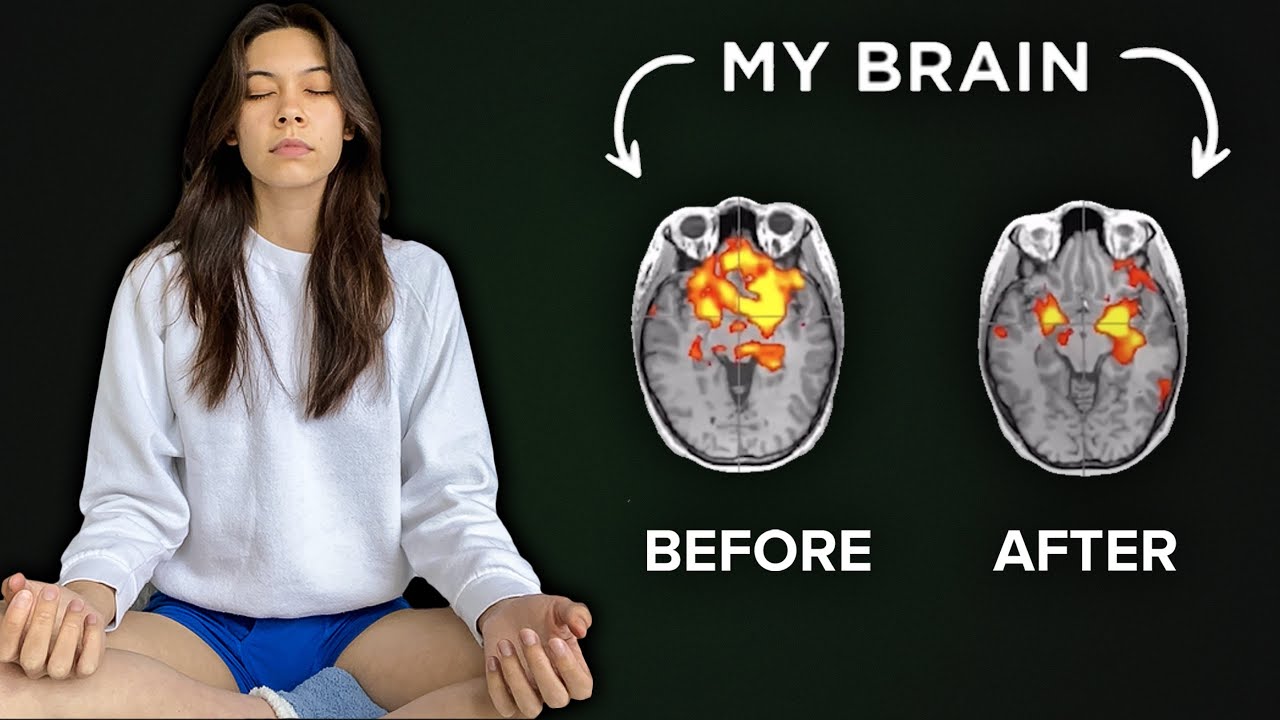
2. How Meditation Changes the Brain
Why It Matters: Understanding the neurological changes induced by meditation provides insight into its therapeutic benefits.
Neuroplasticity:
- Definition: Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
- Meditation’s Role: Regular mindfulness practice enhances neuroplasticity, leading to structural and functional changes in the brain.
Structural Changes:
- Increased Gray Matter: Studies have shown that meditation can increase gray matter density in brain regions associated with learning, memory, and emotional regulation, such as the hippocampus.
- Cortical Thickness: Long-term meditators have increased cortical thickness in areas responsible for attention, sensory processing, and perception.
- Amygdala Shrinkage: The amygdala, the brain’s fight-or-flight center, tends to shrink with consistent meditation practice, resulting in reduced reactivity to stress.
Functional Changes:
- Enhanced Connectivity: Meditation improves connectivity between different brain regions, enhancing overall brain function and communication.
- Improved Default Mode Network (DMN): The DMN is a network of brain regions active when the mind is at rest and not focused on the outside world. Meditation reduces activity in the DMN, associated with self-referential thoughts and mind-wandering, leading to improved focus and attention.
3. Benefits of Meditation on Mental Health
Why It Matters: The mental health benefits of meditation are well-documented, making it a valuable practice for improving psychological well-being.
Reduction in Stress and Anxiety:
- Mechanism: Meditation lowers cortisol levels, the body’s primary stress hormone, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety.
- Evidence: Research shows that mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) programs significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety and stress in various populations.
Improved Emotional Regulation:
- Mechanism: Meditation strengthens the prefrontal cortex, the brain region responsible for executive functions and emotional regulation, and weakens the amygdala’s influence.
- Evidence: Studies indicate that regular meditators exhibit greater emotional stability and resilience in the face of stressors.
Alleviation of Depression:
- Mechanism: Meditation increases the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are linked to mood regulation.
- Evidence: Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) has been shown to be effective in preventing relapse in individuals with recurrent depression.
Enhanced Attention and Concentration:
- Mechanism: Meditation practices that focus on attention, such as focused attention meditation, improve the brain’s ability to concentrate and sustain attention over time.
- Evidence: Research indicates that even short-term meditation training can enhance attention and cognitive control.
READMORE: Beginner’s Guide to Meditation: Simple Techniques to Get Started
Improved Memory and Learning:
- Mechanism: Meditation increases the size and function of the hippocampus, which plays a crucial role in memory formation and learning.
- Evidence: Studies have found that meditators have better working memory capacity and cognitive flexibility compared to non-meditators.
4. Practical Tips for Incorporating Meditation into Daily Life
Why It Matters: Consistency is key to reaping the long-term benefits of meditation.
Start Small:
- Begin with Short Sessions: Start with 5-10 minutes a day and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable with the practice.
- Choose a Convenient Time: Find a time that works best for you, whether it’s first thing in the morning, during a lunch break, or before bed.
Create a Routine:
- Consistency is Key: Meditate at the same time each day to build a habit.
- Set a Reminder: Use alarms or apps to remind yourself to meditate.
Find a Comfortable Space:
- Choose a Quiet Spot: Find a place where you won’t be disturbed.
- Make it Comfortable: Use cushions or a chair to sit comfortably, ensuring your posture supports alertness without causing strain.
Use Guided Meditations:
- Follow Along: Guided meditations can provide structure and support, especially for beginners. Apps like Headspace, Calm, and Insight Timer offer various guided sessions.
Be Patient and Kind to Yourself:
- No Judgment: If your mind wanders, gently bring your focus back to your breath or chosen object of meditation.
- Practice Regularly: Understand that meditation is a skill that improves with practice.
5. Conclusion
The science of meditation reveals profound impacts on the brain, enhancing mental health and overall well-being. By understanding how mindfulness meditation transforms brain structure and function, we can appreciate its potential as a powerful tool for stress reduction, emotional regulation, and cognitive improvement. Starting with short, consistent sessions and gradually incorporating meditation into daily life can lead to lasting benefits. Remember, patience and persistence are key as you embark on your meditation journey.